WHAT IS CROHN’S DISEASE?
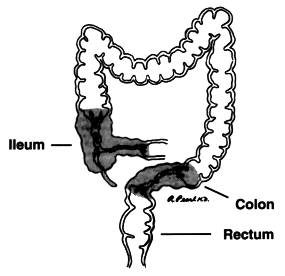 Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory process primarily involving the intestinal tract. Although it may involve any part of the digestive tract from the mouth to the anus, it most commonly affects the last part of the small intestine (ileum) and/or the large intestine (colon and rectum).
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory process primarily involving the intestinal tract. Although it may involve any part of the digestive tract from the mouth to the anus, it most commonly affects the last part of the small intestine (ileum) and/or the large intestine (colon and rectum).
Crohn’s disease is a chronic condition and may recur at various times over a lifetime. Some people have long periods of remission, sometimes for years, when they are free of symptoms. There is no way to predict when a remission may occur or when symptoms will return.
What are the symptoms of Crohn’s disease?
Because Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the intestine, symptoms may vary greatly from patient to patient. Common symptoms include cramping, abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, weight loss, and bloating. Not all patients experience all of these symptoms, and some may experience none of them. Other symptoms may include anal pain or drainage, skin lesions, rectal abscess, fissure, and joint pain (arthritis).Common Crohn’s symptoms:
Who Does it Affect?
Any age group may be affected, but the majority of patients are young adults between 16 and 40 years old. Crohn’s disease occurs most commonly in people living in northern climates. It affects men and women equally and appears to be common in some families. About 20 percent of people with Crohn’s disease have a relative, most often a brother or sister, and sometimes a parent or child, with some form of inflammatory bowel disease.Crohn’s disease and a similar condition called ulcerative colitis are often grouped together as inflammatory bowel disease. The two diseases afflict an estimated two million individuals in the U.S.