Colorectal cancer is the second most common cancer in the United States, striking 140,000 people annually and causing 60,000 deaths. That’s a staggering figure when you consider the disease is potentially curable if diagnosed in the early stages.
Who is at Risk?
Though colorectal cancer may occur at any age, more than 90% of the patients are over age 40, at which point the risk doubles every ten years. In addition to age, other high risk factors include a family history of colorectal cancer and polyps and a personal history of ulcerative colitis, colon polyps or cancer of other organs, especially of the breast or uterus.
How Does it Start?
It is generally agreed that nearly all colon and rectal cancer begins in benign polyps. These pre-malignant growths occur on the bowel wall and may eventually increase in size and become cancer. Removal of benign polyps is one aspect of preventive medicine that really works!
What are the Symptoms?
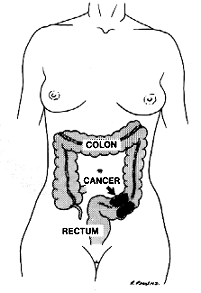 The most common symptoms are rectal bleeding and changes in bowel habits, such as constipation or diarrhea. (These symptoms are also common in other diseases so it is important you receive a thorough examination should you experience them.) Abdominal pain and weight loss are usually late symptoms indicating possible extensive disease.
The most common symptoms are rectal bleeding and changes in bowel habits, such as constipation or diarrhea. (These symptoms are also common in other diseases so it is important you receive a thorough examination should you experience them.) Abdominal pain and weight loss are usually late symptoms indicating possible extensive disease.